杨肖研究室
Yang Group
研究 Research
化学元素是构成物质世界的基本单元,元素的利用决定了人类文明的存续和发展。我们关注化学元素的分离与回收,承继先人的智慧与品味,从无价中提取有价,探索从复杂中获得纯粹的最优方法,洞悉物质变换的内在规律。
Chemical elements play a fundamental role in shaping every aspect of human civilization. To deepen our understanding of material transformation, we are actively developing innovative processes for extracting pure elements from complex systems. These endeavors allow us to gain valuable insights into the nature of matter and its transformative properties.

熔盐体系中含氧酸根离子的物理化学
Physical chemistry of oxyanions in molten salts
元素周期表的13族至16族多个元素都具有半导体特性,电负性介于常见的金属和非金属之间,易与氧结合形成含氧酸根离子,如硼酸根、硅酸根、磷酸根、硒酸根等。我们发现,这些含氧酸根离子在氯化钙熔盐中普遍具有较高的溶解度。我们的研究由此展开,试图系统揭示氯化钙熔盐体系中含氧酸根离子的形成、传质、结构以及电化学反应等基础物理化学特性,为元素提取或回收的新工艺开发提供理论指导。
Multiple elements in the periodic table groups 13-16 possess semiconductor properties. They usually bind with O to form oxyanions, such as borate, silicate, phosphate and selenate. Our research has revealed that all these oxyanions exhibit solubility in molten CaCl2. Accordingly, we focus on elucidating the physical chemistry of oxyanions in molten CaCl2, including formation mechanism, mass transfer, microstructure and electrochemical behavior. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these phenomena, we aim to establish a solid foundation for the development of novel processes for elements extraction or recycling. Our ultimate goal is to contribute to the advancement of sustainable and efficient methods in the field of element utilization.
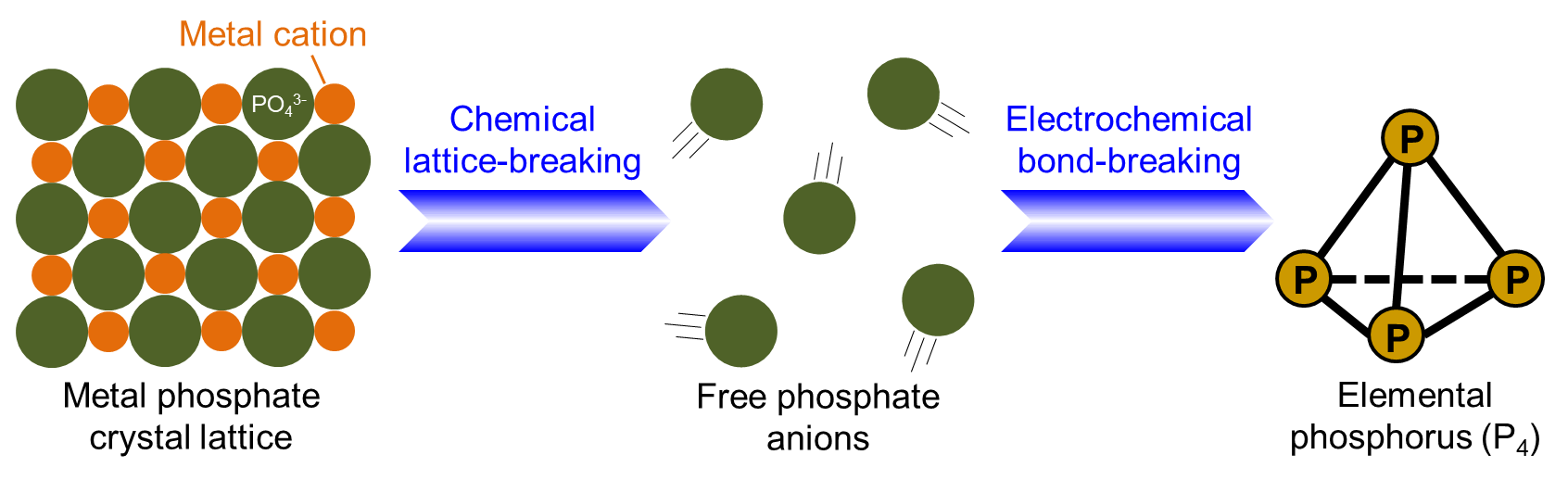
电化学提取单质磷元素 (P4)
Electrochemistry isolates elemental phosphorus
1669年德国炼金术士Brandt用碳热还原法从尿液蒸馏物中首次提取单质磷元素,为人类开启了一个现代化学的时代。
2019年我们发明了电化学提取磷元素的方法,正在努力使其变成一种可以实用的清洁生产技术,解决人类未来可能面临的磷资源短缺危机。
In 1669, a significant breakthrough occurred in chemistry when a German alchemist named Brandt successfully discovered elemental phosphorus. This groundbreaking achievement was accomplished through carbothermic reduction of urine distillate.
Fast-forward to 2019, where our research team developed an innovative method for the isolation and recycling of elemental phosphorus from phosphate-bearing solids. Our approach involves the utilization of electrochemistry, a technique that harnesses electrical energy to drive chemical transformations.

资料 Reference
* https://advanceseng.com/electrochemistry-enables-cleaner-production-white-phosphorus/
* Yao YU and Xiao YANG*, “Dissolution of Solid FePO4 in Molten CaCl2”, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, In Press (2024)
* Guanting LIU, Yuanjia Ma, and Xiao YANG*, “Cleaner extraction of white phosphorus from phosphate rock through molten salt electrolysis”, J. Cleaner Prod., 434 (2024), 140374.
* Yuxiang ZHONG, Guanting LIU, and Xiao YANG*, "Isolating Elemental Phosphorus from Sewage Sludge Ash by Electrochemistry", Resources, Conservation & Recycling,190(2023), 106815.
* Guanting LIU, Yuxiang Zhong, and Xiao YANG*, “Electrolysis of Dissolved Phosphate in Molten CaCl2 Prepares High-Purity White Phosphorus”, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 54 (2023), 2277-2282.
* Y. ZHONG and X. YANG*, “Dissolution Behavior of Solid Ca3(PO4)2 in molten CaCl2”, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 52 (2021), 3515-3523.
* X. YANG* and T. NOHIRA, “A New Concept for Producing White Phosphorus: Electrolysis of Dissolved Phosphate in Molten Chloride”, ACS Sus. Chem. Eng., 8 (2020), 13784-13792.
从下水道污泥灰中电化学提取单质磷元素的动画过程(点击播放)
A video showing the process of isolating P4 from sewage sludge ash by electrochemistry (click and play)